A hypertonic or overactive pelvic floor (distinct from an overactive bladder) results from the buildup of excessive tension within the muscles. In this situation, the pelvic floor can also be referred to as "tight", which is often wrongly believed to be a good thing. This article will debunk this myth and shed light on the misconceptions surrounding this topic. Delving into the consequences of such a condition, we will also explore the common errors that can lead to a hypertonic pelvic floor and provide effective and practical strategies to address it.
Table of contents
- An overview of the characteristics of a hypertonic pelvic floor
- A hypertonic pelvic floor can't relax and stretch open
- Excessive pelvic floor tension and incontinence
- Intra-abdominal pressure management with a hypertonic pelvic floor
- The consequences of a hypertonic pelvic floor on the sexual sphere
- The types of pelvic floor exercises to consider with a hypertonic pelvic floor
- The additional solutions to address excessive pelvic floor tension
- Taking actions to tackle a hypertonic pelvic floor
An overview of the characteristics of a hypertonic pelvic floor
A hypertonic pelvic floor exhibits several characteristics that hinder its optimal functioning. The most noticeable one is the inability to relax and stretch. This directly impacts the "opening mode" of the gate control function, which is responsible for releasing urine and stool and allowing passage for intercourse and childbirth.
Surprisingly, a hypertonic pelvic floor also affects the "closing mode" of the gate control and the support functions that maintain continence and keep the pelvic organs in place. Indeed, the excess tension restricts mobility, leaving the muscles stuck and unable to not only stretch but also effectively contract.
Moreover, this constant tension leads to muscular fatigue, reducing the capacity to generate fast and strong contractions when needed. Essentially, the muscles are overworked and unable to provide much more when required. It is fair to consider that a hypertonic muscle is weak.
It is evident that a hypertonic pelvic floor, unable to lengthen properly and contract effectively, faces even greater challenges when attempting both actions simultaneously. A healthy muscle should be capable of contracting while its fibres lengthen, known as an eccentric contraction. It is distinct from concentric contractions, which is what people usually have in mind, where the fibres only shorten. Eccentric contractions demand a combination of strength and elasticity, both of which are lacking in overly tense muscles.
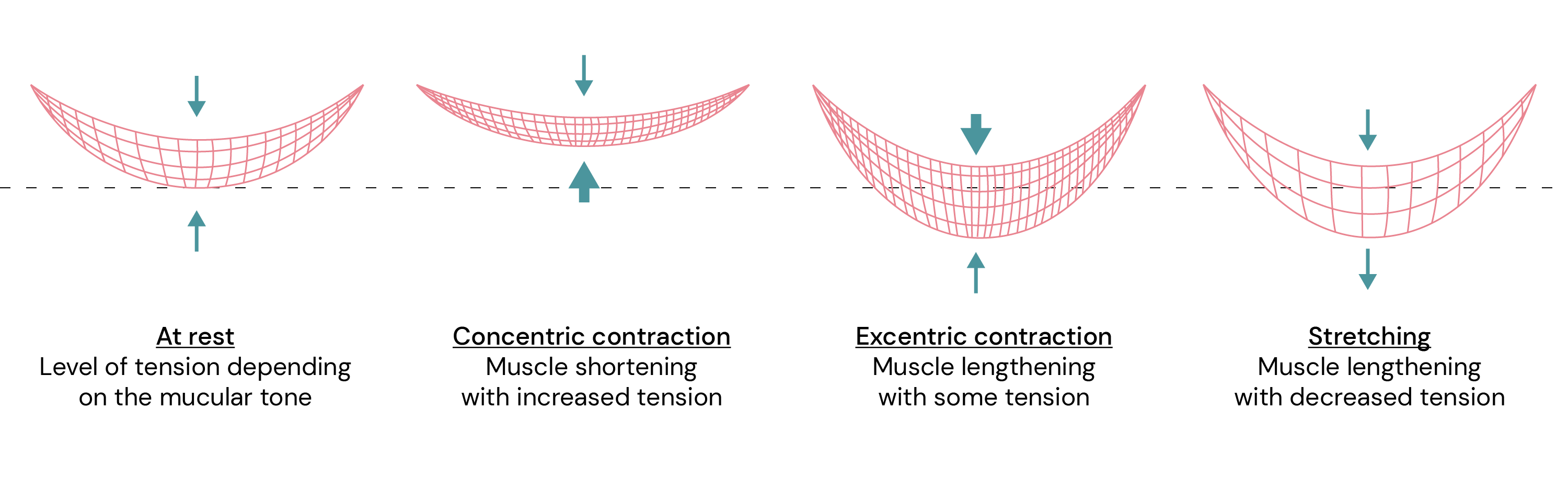
Now, let's explore how these characteristics lead to pelvic floor dysfunctions.
A hypertonic pelvic floor can't relax and stretch open
As explained above, excess tension affects the opening mode of the gate control function. In simpler terms, the sphincters of a hypertonic pelvic floor may struggle to open up correctly. It can lead to issues with bladder emptying (resulting in urinary obstruction and/or retention) and bowel movements (leading to outlet constipation).
Additionally, the over-tensed muscles can hinder the vaginal canal from stretching properly, increasing the likelihood of difficult childbirth and causing painful intercourse (more details will be provided below).
Beyond these apparent issues, a hypertonic pelvic floor can give rise to various other complications that may not be immediately obvious. However, we will endeavour to explain them as clearly as possible in the following sections.
Excessive pelvic floor tension and incontinence
Many people believe that lack of muscular tone is the sole cause of incontinence. Against all odds, excessive tone can also be behind this issue.
Firstly, the inability of the sphincters to open up correctly can lead to overflow incontinence. It occurs when the bladder becomes full and can't empty properly, causing pressure to build up and resulting in leakage. The same can happen with the bowel, leading to passive incontinence, also called soiling.
Secondly, the rigidity and fatigue of the muscles prevent the sphincters from contracting effectively, potentially leading to stress incontinence. Ideally, the muscular tone should dynamically adjust to accommodate current demands. However, in the case of a hypertonic pelvic floor, the muscles are exhausted and unresponsive, remaining "stuck" in a fixed state. They can't adapt to increased strain by contracting as needed to counter the opposing forces. Consequently, the sphincters (the "lock" muscles) may fail, resulting in accidental leakage when facing elevated pressure, such as sneezing, coughing, or lifting heavy objects.
Intra-abdominal pressure management with a hypertonic pelvic floor
As mentioned earlier, eccentric contractions cannot occur correctly with a hypertonic pelvic floor. However, this mechanism is essential to manage intra-abdominal pressure.
When the pelvic floor eccentrically contracts, it remains activated to fulfil its supportive role and maintain sphincters' closure while the fibres stretch under control.
This controlled lengthening of the muscles at the bottom of the abdominal cavity increases volume, thereby reducing pressure. This effective strategy minimises the downward forces instead of requiring the pelvic floor to contract excessively to resist them.
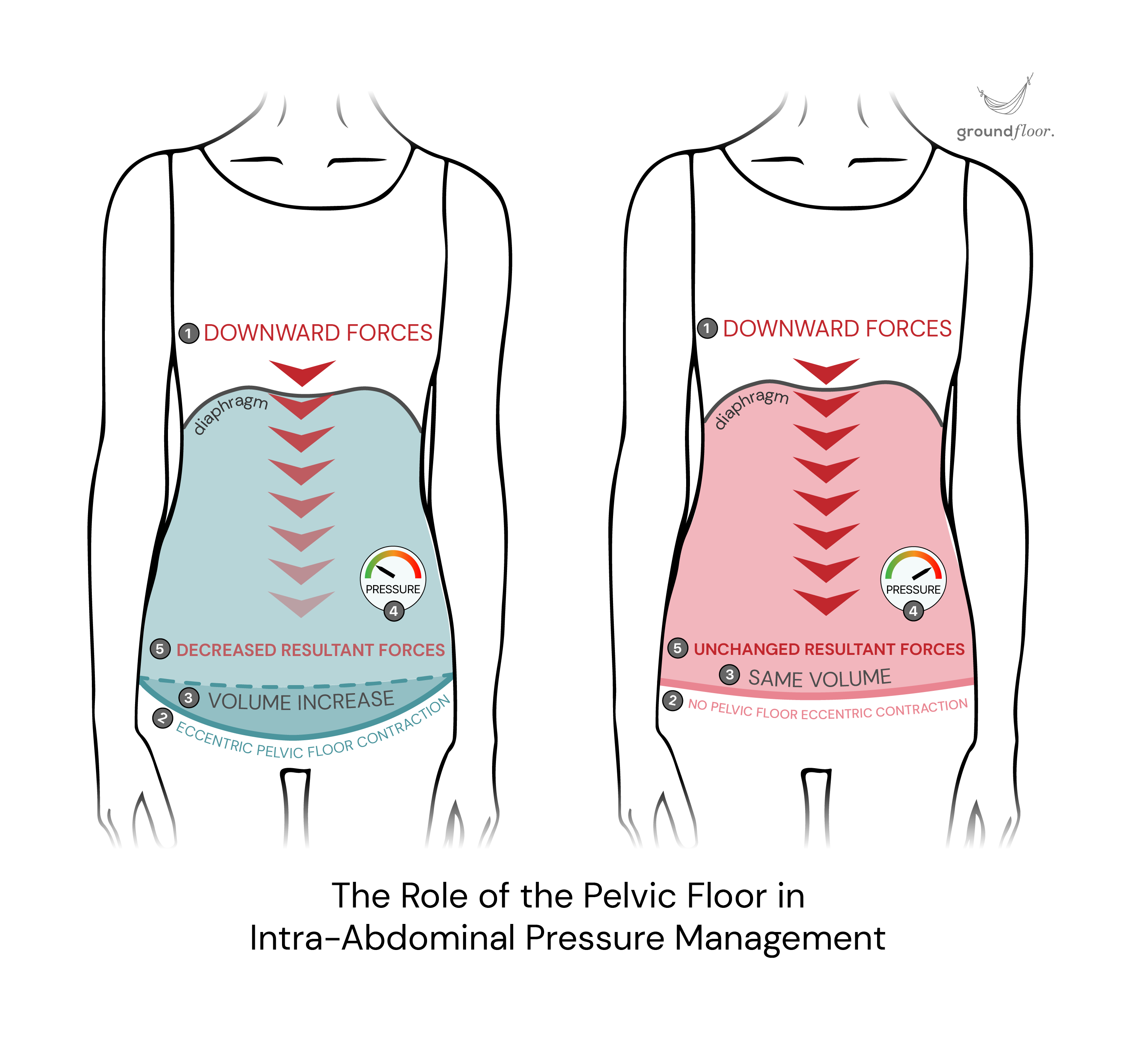
This intelligent mechanism conserves energy and provides long-term protection for your pelvic floor. Under normal circumstances, it occurs frequently and ideally coincides with each inhalation when following an optimal breathing pattern.
A hypertonic pelvic floor unable to eccentrically contract will suffer the consequences of unmanaged intra-abdominal pressure and excessive downward strain. This situation creates a favourable environment for the development of pelvic organ prolapse and stress incontinence.
The consequences of a hypertonic pelvic floor on the sexual sphere
Excessive muscle tone leads to a notable decline in mobility, limiting the ability to contract and stretch adequately—a circumstance that can give rise to various issues in the sexual sphere.
When a hypertonic pelvic floor is "stuck" in a mid-range position, it loses the capacity to tighten effectively to accommodate the size and shape of a penis or any object during penetrative intercourse. This lack of flexibility can result in reduced sensations during sex and difficulty achieving orgasm. It is worth noting that while weakness and reduced tone can also contribute to this issue, they aren't always the primary cause. This underscores the importance of a thorough pelvic health check-up before embarking on any exercise regimen, ensuring it suits your individual needs.
Predictably, discomfort stemming from the struggle to release tension and achieve relaxation is the most prevalent symptom of a hypertonic pelvic floor. This incapacity to stretch and relax appropriately can result in pain during sexual intercourse (known as dyspareunia), discomfort while inserting a tampon, soreness around the tailbone, and unease when sitting or during specific movements. In some instances, this pain might extend to the groin area or lower back.
In extreme cases, a condition called vaginismus can occur, wherein the pelvic floor muscles suddenly tighten further when attempting vaginal penetration. It is highly painful (dyspareunia) and can even make penetration impossible (apareunia).
Similarly, the same reflex contraction can affect the anus, known as anismus (or puborectalis syndrome). This condition can severely interfere with bowel evacuation, leading to outlet constipation and often causing injuries like haemorrhoids or anal fissures.
Both vaginismus and anismus are automatic responses and can stem from traumatic experiences or underlying issues such as anxiety, fear, negative beliefs about sex, a history of abuse, or uncomfortable/painful past experiences.
The types of pelvic floor exercises to consider with a hypertonic pelvic floor
The primary objective when dealing with a hypertonic pelvic floor is to alleviate the excessive tension and promote muscle relaxation. This imperative drives the inclusion of numerous exercises within the app, all designed to facilitate this crucial aim. However, a more comprehensive approach is essential to fully address this intricate issue.
As explained above, from a technical standpoint, a hypertonic pelvic floor also presents signs of muscular weakness. Nevertheless, typical kegel exercises are not suitable until the tension has been effectively reduced.
In fact, at this stage, Kegels can even worsen the situation. Indeed, they primarily involve concentric contractions without emphasising eccentric work or elongation. Repetitive shortening of the muscles would reinforce their rigidity, which contradicts the long-term goal of relaxing and lengthening the pelvic floor.
Suppose you are concerned by a hypertonic pelvic floor. In that case, the initial focus should predominantly be on fostering muscle relaxation and gaining awareness. The following steps must include strengthening exercises incorporating eccentric work to maintain newfound flexibility.
Strategically training your pelvic floor with different modalities at the right time is crucial. This is why the functional progression of your tailored training always adapts to your needs and pace to ensure you work the right way.
It is worth mentioning that eccentric strength is an important characteristic for everyone, not solely those with a hypertonic pelvic floor. This modality is included in the advanced exercises of each program to ensure that no individual misses the opportunity to cultivate this essential quality and prevent muscular tension development.
The additional solutions to address excessive pelvic floor tension
Any behaviour that doesn't allow the muscle to relax and let go, compelling it to remain continuously contracted or switched "on" for too long, can contribute to the development of a hypertonic pelvic floor. Factors such as stress and anxiety unconsciously trigger tension in this area, as does holding on to the bladder or bowel for extended periods.
Ground Floor App includes breath work, vagal stimulation, and stretching routines to offer a comprehensive program that targets multiple dimensions of this issue. Additionally, the habits tracker feature aids in transforming behaviours that contribute to pelvic floor tension.
It's important to recognise that several other circumstances can contribute to muscular tension in the pelvic region. Chronic pelvic pain, digestive issues, painful bladder syndrome (interstitial cystitis), endometriosis, and psychological and physical traumas, among others, play a role. If you are grappling with any of these health issues, addressing them can significantly improve the state of your pelvic floor.
Taking actions to tackle a hypertonic pelvic floor
Having a hypertonic pelvic floor is more prevalent than one might realise. While this concern has gained more attention in recent years, it often comes to light only in connection with common symptoms such as pelvic pain or dyspareunia. However, now you understand that it can manifest in numerous forms, at times subtly, and can be associated with unexpected dysfunctions.
It's important to emphasise that a hypertonic pelvic floor is not a fatality, as several solutions are available to address this issue. By taking the check-up, you can assess the degree of tension in your pelvic floor and access a tailored program designed to assist you if you happen to be dealing with excessive muscle tension. Even if you're not, the program will provide insights into preventing this situation from affecting you. Through the check-up, you will also have the opportunity to identify many other pelvic floor dysfunctions and take charge of your health.
Share this article with your friends and help spread the knowledge together! ↓
Share this article with your friends and help spread the knowledge together! →





Download the app to learn more about this topic and receive tailored information about your pelvic health!


Related articles
6 min read
Rise above the pressure: Reinforce your pelvic support system!Discover the vital importance of the pelvic floor's support function, a topic often neglected but essential for optimal pelvic health. This article will give you insights into caring for your pelvic floor, effectively preventing problems associated with an impaired support system. Armed with this knowledge, you can proactively reduce the risk of issues such as pelvic organ prolapse and perineum descent.
→ Read more
7 min read
Pelvic floor & bowel control: from constipation to incontinence! In the realm of pelvic health, urinary concerns often take the spotlight, leaving many surprised to discover the intricate involvement of the pelvic floor in bowel movement. This article aims to shed light on this lesser-discussed connection, exploring how pelvic floor dysfunctions can lead to both constipation and incontinence.
We will begin by explaining the different types of functional constipation. From there, we will delve into the mechanics of bowel control and its potential breakdown, giving rise to constipation and/or incontinence. By the end of this read, you will have a clear grasp of the inner workings of bowel movement physiology and gain insights to make informed choices for your pelvic health.
Let's quickly recall a few notions first. The rectum serves as the faeces storage unit. It is the last part of the large intestine (also called the colon), right before the anus. The ability to hold in your bowels is called continence. In contrast, incontinence is when you lose bowel control and have an accidental leakage.
→ Read more
10 min read
Unlocking pleasure: Your pelvic floor's secret to fulfilling sex!Experiencing pain during intercourse? Struggling with sensations or achieving orgasm? Contrary to common beliefs, many sexual dysfunctions are not psychogenic or hormonal in nature. Instead, they often stem from pelvic floor issues. This article will uncover strategies to improve your pelvic health while elevating your sexual life to unprecedented levels.
To start, we will explore the anatomy of the clitoris, its relationship with the pelvic floor, and their roles in the context of sexual activities. Then, we will explore prevalent dysfunctions and conditions that contribute to these challenges and provide insights into effective approaches for resolution. Finally, we will delve into the intricate interplay of physical, mental, and emotional factors within the multifaceted realm of sexuality.
→ Read more

